Causes of the Civil War |
|
This huge section of LearnaboutAmerica.com includes articles, activities, interactives, and printables on all of the major causes of the Civil War. The word "MAJOR" after a link indicates it as an ESSENTIAL cause of the war. |
|
 |
Slavery in America - MAJOR
Slavery was a central cause of the Civil War, as it created deep economic, political, and moral divisions between the Northern and Southern states. Southern states relied on enslaved labor for their agricultural economy and sought to protect and expand the institution. |
 |
The Invention of the Cotton Gin The invention of the cotton gin greatly increased the profitability of cotton farming, leading to a rapid expansion of slavery in the Southern states. This growth in slavery deepened the divide between the North and South, contributing to the tensions that eventually led to the Civil War. |
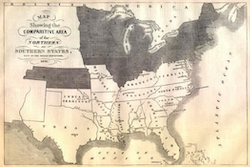 |
The Missouri Compromise of 1820 temporarily resolved the issue of slavery's expansion by admitting Missouri as a slave state and Maine as a free state, while banning slavery in new territories north of 36° 30' latitude. However, it highlighted the deepening sectional divide between the North and South, setting the stage for further conflict over slavery. |
 |
The Nat Turner Rebellion of 1831 shocked the South and intensified fears of slave uprisings, leading to harsher laws that further restricted the rights of enslaved people. This deepened the divide between North and South over the issue of slavery, contributing to the growing tensions that eventually led to the Civil War. |
 |
Harriet Tubman and the Underground Railroad Harriet Tubman and the Underground Railroad helped expose the cruelty and injustice of slavery by actively resisting it and guiding enslaved people to freedom. Her actions, and those of others like her, increased tensions between the North and South, as Southern slaveholders saw the loss of their "property" as a direct threat—fueling the growing conflict that led to the Civil War. |
 |
Manifest Destiny - MAJOR Manifest Destiny was the belief that the United States was meant to expand westward across the continent. As new territories were added, fierce debates over whether slavery would be allowed in these areas increased tensions between the North and South, helping lead to the Civil War. |
 |
The Free Soil Movement opposed the expansion of slavery into new western territories, arguing that land should be reserved for free white labor. This stance angered Southern leaders who saw it as a threat to slavery and their political power, increasing sectional tensions that helped lead to the Civil War. |
 |
Compromise of 1850 - MAJOR The Compromise of 1850 temporarily eased tensions between free and slave states by balancing interests, but its enforcement of a stricter Fugitive Slave Law angered many in the North. While it delayed secession, the compromise deepened sectional divides and set the stage for future conflicts, making civil war more likely. |
 |
Radical vs Moderate Abolitionists As the path to the Civil progressed, two types of abolitionists emerged: Radical and Moderate. While both supported the end of slavery, radical abolitionists believed that slavery had to be abolished at all costs, even if it meant war. |
 |
Harriet Beecher Stowe and Uncle Tom's Cabin - MAJOR Harriet Beecher Stowe's landmark novel awoke the Northern public to the horrors of slavery in South and caused further conflict between the two sides. |
 |
The Ostend Manifesto increased tensions between the North and South by proposing the U.S. purchase or seize Cuba, which many Southerners hoped would become a new slaveholding territory. |
 |
Kansas-Nebraska Act - MAJOR The Kansas-Nebraska Act of 1854 allowed settlers in those territories to decide for themselves whether to allow slavery, effectively repealing the Missouri Compromise. This led to violent conflict in "Bleeding Kansas" and intensified national tensions over slavery, pushing the country closer to civil war. |
 |
Bleeding Kansas and the Pottawatomie Massacre - MAJOR The Pottawatomie Massacre, led by abolitionist John Brown in 1856, involved the brutal killing of five pro-slavery settlers in Kansas. This violent act deepened the hostility between North and South, contributing to the growing unrest that eventually led to the Civil War. |
 |
Dred Scott Decision - MAJOR The Dred Scott decision ruled that enslaved people were not citizens and had no legal rights, and it declared that Congress could not ban slavery in U.S. territories. This outraged many in the North, deepened the divide between free and slave states, and pushed the nation closer to civil war. |
 |
The Wilmot Proviso proposed banning slavery in any new territories gained from the Mexican-American War, which angered Southern leaders who wanted slavery to expand westward. This deepened the divide between North and South and contributed to the rising tensions that eventually led to the Civil War. |
 |
John Brown Rebellion - MAJOR John Brown's 1859 raid on the federal arsenal at Harpers Ferry was an attempt to spark a slave rebellion and directly challenged the institution of slavery. His violent actions and execution deepened the divide between North and South, convincing many Southerners that abolitionists would stop at nothing, helping to push the nation closer to civil war. |
 |
The caning of Senator Charles Sumner in 1856 shocked the nation, as it showed how deeply divided the country had become over slavery. The violent attack in the U.S. Senate increased tensions between the North and South, pushing the nation closer to civil war. |
 |
The Lincoln-Douglas debates of 1858 highlighted the deep national divide over slavery, with Lincoln opposing its expansion and Douglas defending popular sovereignty. These public debates intensified sectional tensions and helped shape the political conflict that would eventually lead to the Civil War. |
 |
Lincoln’s Cooper Union speech clarified the Republican Party’s firm stance against the expansion of slavery, challenging the South’s demands for its spread into new territories. By framing slavery as morally and historically wrong, the speech deepened sectional divisions and increased Southern fears, helping to set the stage for the Civil War. |
 |
Partisan Politics of the Civil War Era Partisan politics during the Civil War era deepened national divisions, as political parties became increasingly split over the issue of slavery. The breakdown of compromise between Democrats, Republicans, and other parties made it nearly impossible to find common ground, pushing the nation toward secession and war. |
 |
Republican National Convention of 1860 The Republican National Convention of 1860 marked the rise of a political party firmly opposed to the expansion of slavery, with the nomination of Abraham Lincoln symbolizing a clear challenge to Southern interests. Lincoln’s selection deepened sectional tensions and led many Southern states to view his potential presidency as a threat, prompting the move toward secession and ultimately the Civil War. |
 |
Election of 1860 - MAJOR The election of Abraham Lincoln in 1860, without any electoral support from Southern states, underscored the deep sectional divide over slavery and states' rights. His victory prompted seven Southern states to secede from the Union before his inauguration, setting the stage for the American Civil War. |
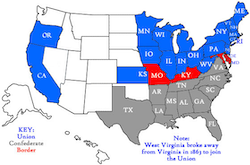 |
Secession of the Southern States - MAJOR The secession of Southern states in 1860 and 1861, initiated by South Carolina, was a direct response to the election of Abraham Lincoln, whose anti-slavery stance threatened the institution central to the Southern economy and way of life. This collective withdrawal from the Union led to the formation of the Confederate States of America, setting the stage for the outbreak of the Civil War. |
 |
The Border States—Delaware, Maryland, Kentucky, and Missouri—were crucial to the Civil War because they provided vital resources, strategic locations, and large populations with divided loyalties. Their decision to remain in the Union helped prevent the Confederacy from gaining a significant military and political advantage. |